Description
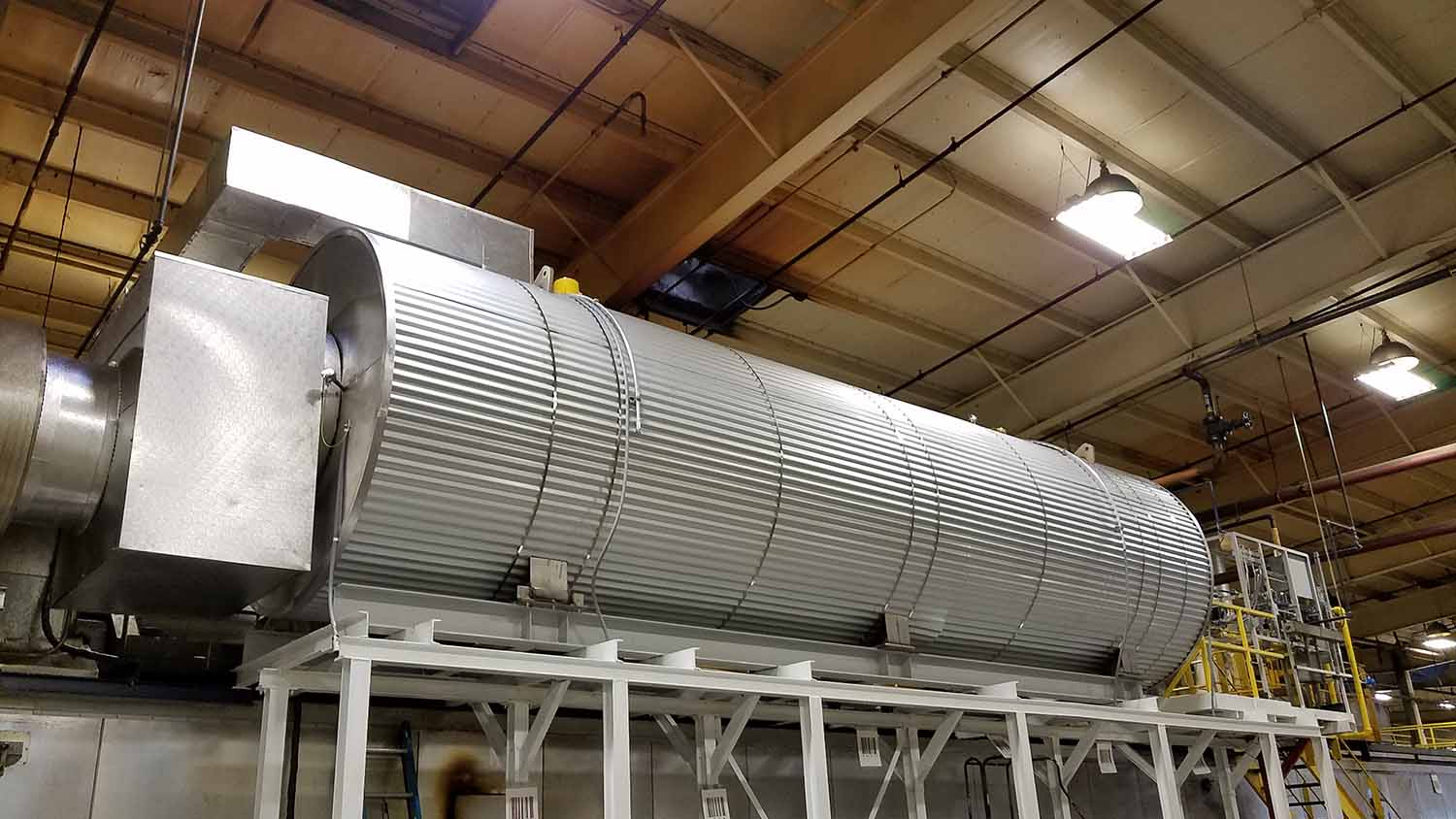
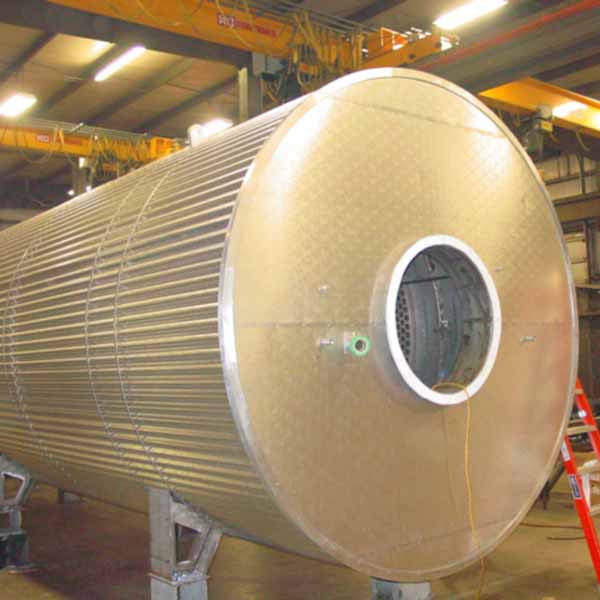
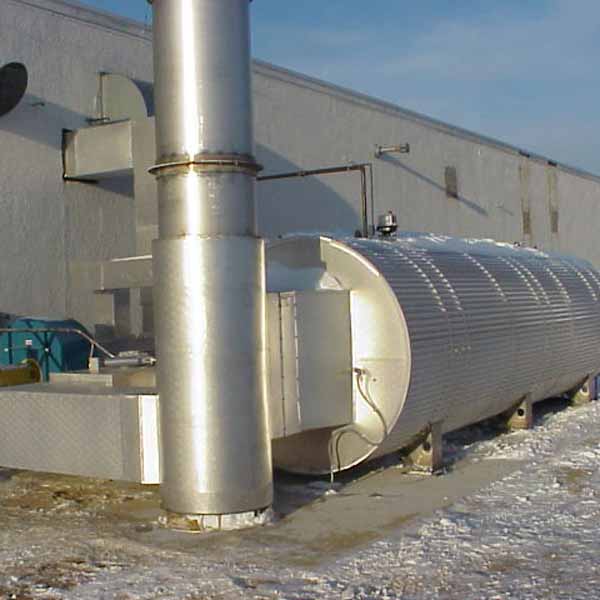
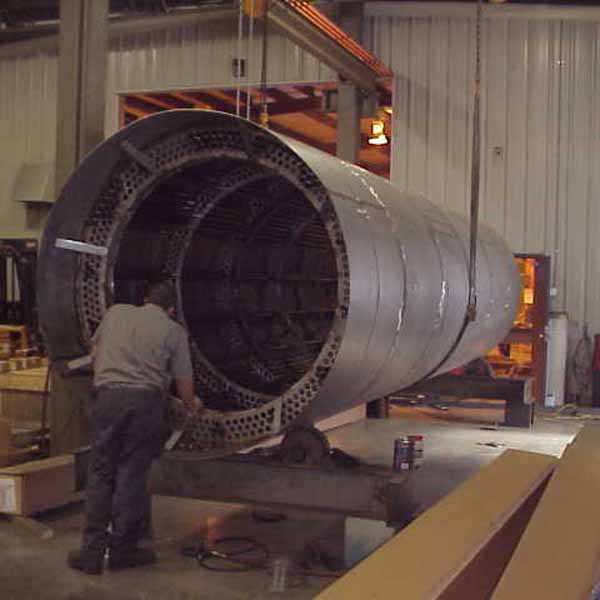
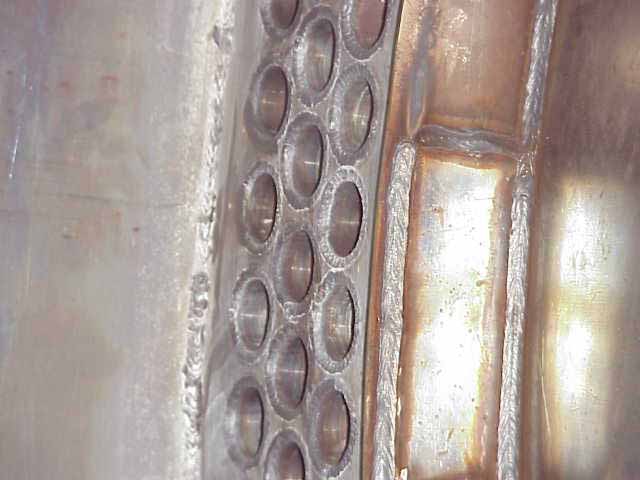
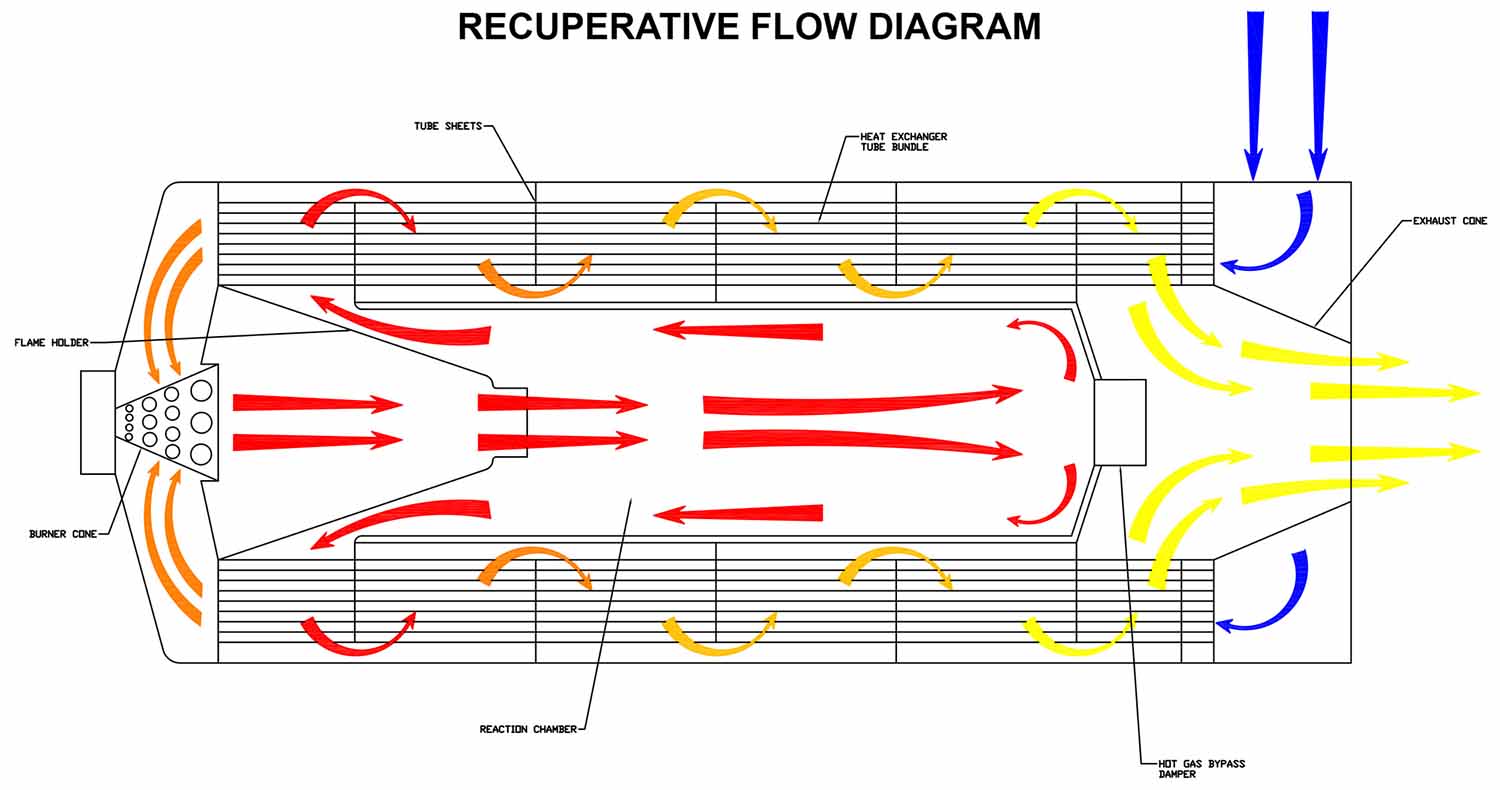
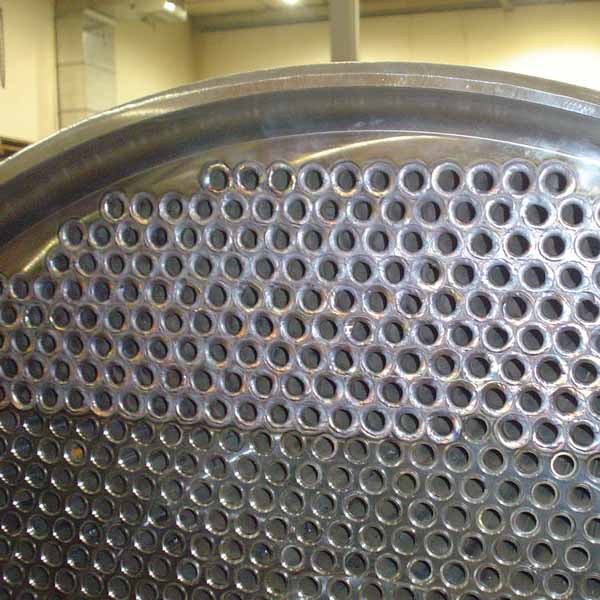
Recuperative thermal oxidizers use a stainless steel heat exchanger to preheat the incoming process air to within 400°F of the combustion temperature prior to entering the combustion chamber. The burner will provide the remaining energy to heat the process air to the combustion chamber temperature of ~1,400°F. In the combustion chamber, the VOCs within the process exhaust will convert to CO2 and H2O. This 1,400°F air, now clean, will pass through the opposite side of the heat exchanger, thus providing the energy for the incoming process air. Most recuperative oxidizers will utilize a shell and tube style heat exchanger. The shell and tube design will provide a longer life and provide access for cleaning if needed. Recuperative heat exchangers can have thermal efficiencies from 40% to 80% depending on the application.
Although regenerative oxidizers account for the majority of oxidizer sales in today’s market, recuperative oxidizers still have a place in the pollution control industry. Below are some applications where recuperative oxidizers work better than others.